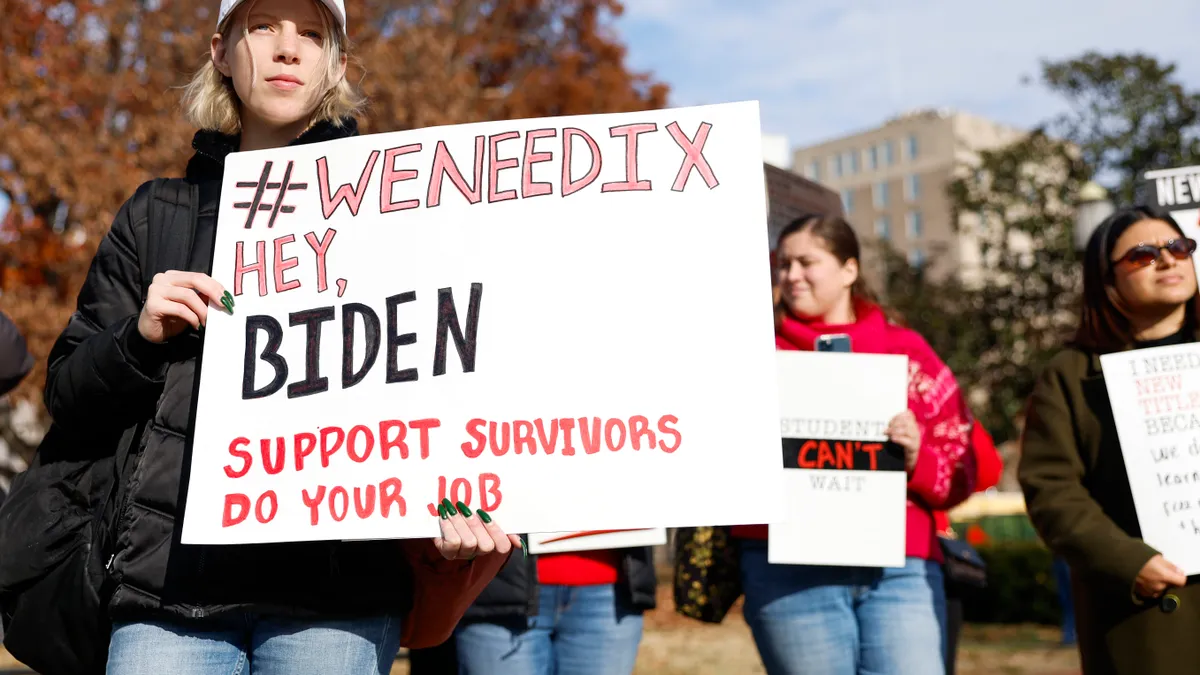The U.S. Department of Education began enforcing its new Title IX rule protecting LGBTQI+ students on Aug. 1, changing how schools investigate and resolve sex discrimination complaints for the third time in three administrations.
The final regulations "clarify that Title IX's prohibition of sex discrimination includes all forms of sex discrimination," said U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona during a webinar that morning. "Because it's unacceptable that any student has to give up on their dreams of a college degree because they're pregnant, and it's unacceptable that any student faces discrimination or bullying because of who they are."
The rule has been controversial to say the least. It ultimately went into effect in just 24 states after being put on pause in more than half the nation due to lawsuits from Republican state attorneys general.
In response, Catherine Lhamon, assistant secretary for the Education Department's Office for Civil Rights, said her office will enforce the old 2020 Title IX rule in the 26 enjoined states.
The fragmented rollout, last-minute injunctions, and 11th-hour clarifications from the Education Department have led to confusion and frustration among K-12 leaders. Read our coverage to learn about the latest developments as the rule is litigated, find best practices on implementation, and understand how this situation is impacting the K-12 community.