The coronavirus pandemic severely disrupted schools, and with President Joe Biden set to end the national COVID-19 emergency declaration Thursday, K-12 Dive created a timeline outlining the key dates that shaped school operations during the last three years.
Feb. 26, 2020
In a telebriefing about a new coronavirus, an official from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said that in a severe pandemic, schools may need to prepare for "internet-based teleschooling to continue education," in order to reduce the spread of the virus.
March 5, 2020
Then-U.S. Education Secretary Betsy DeVos, who was on Capitol Hill to testify about the proposed FY 2021 budget, tells senators the U.S. Department of Education is in daily contact with CDC regarding a new coronavirus that had already begun causing school closures in Oregon and Washington state. DeVos tells lawmakers the department is updating 2009 guidance on providing services to students with disabilities during the H1N1 flu outbreak.
March 13, 2020
Then-President Donald Trump declared a national emergency in regard to COVID-19, retroactive to March 1, 2020. The emergency declaration gives permission for the secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to waive or modify certain requirements of the Medicare, Medicaid and State Children's Health Insurance Program, and of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act Privacy Rule, throughout the duration of the public health emergency. Schools across the country start closing campuses and plan for virtual learning.
March 26, 2020
The U.S. Department of Agriculture announces waivers to the federal child nutrition programs to make it easier for schools to serve meals to students who are not in school buildings. Schools across the country mount an unprecedented effort to coordinate grab-and-go meals while students are learning virtually.
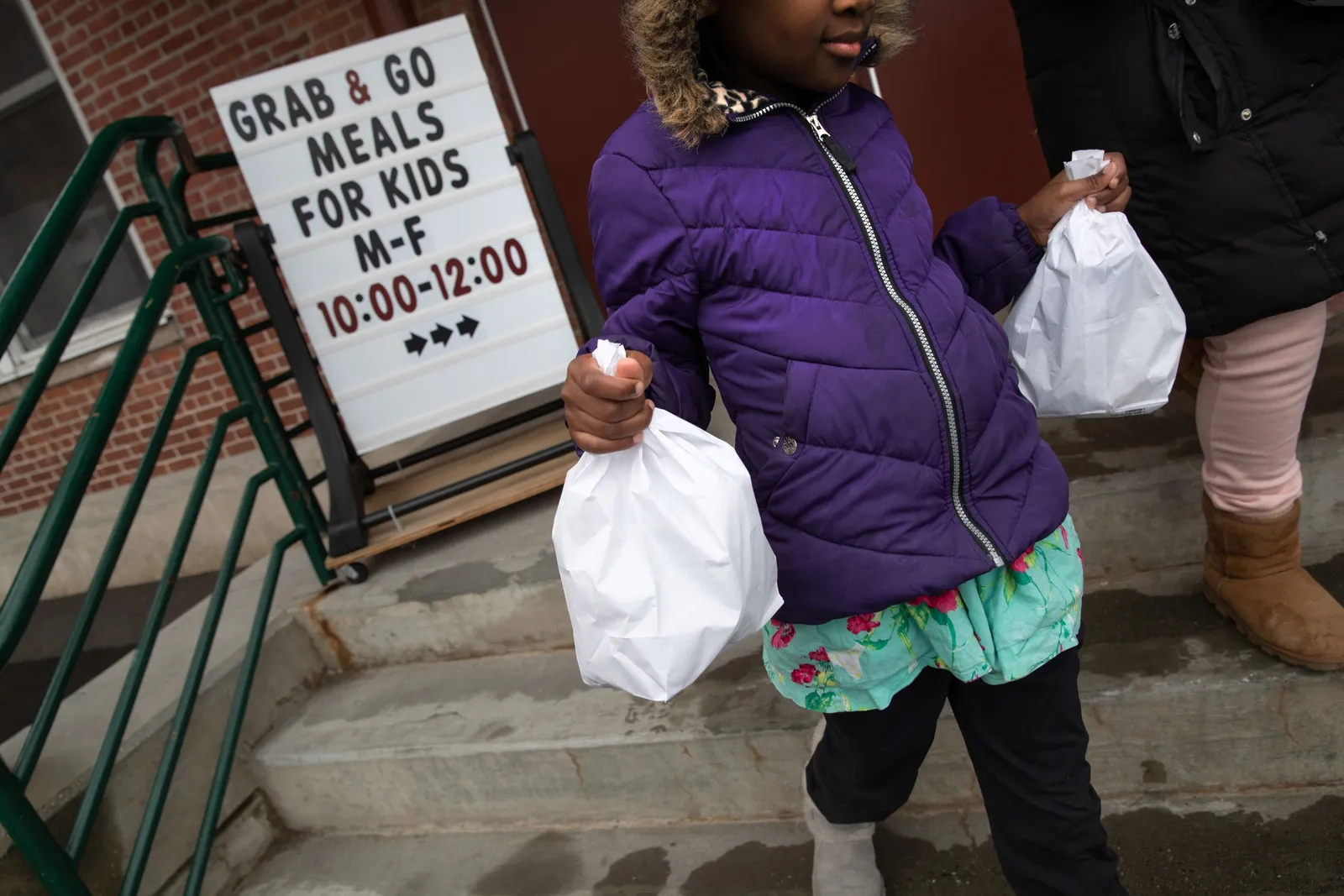
March 25, 2020
Congress passes the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES), which includes the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief fund (ESSER). The $13.2 billion allocation is provided to states to help districts respond to pandemic-related needs, including providing devices and Wi-Fi access for virtual learning and to prepare for safe in-person learning.

May 20, 2020
The CDC issues its first reopening guidance for schools, summer camps and higher education institutions. On July 23, 2020, the CDC issued further guidance for schools planning to reopen in the fall. The recommendations include how to keep school environments healthy through cleaning, proper ventilation, social distancing and other practices.
Fall 2020
A national analysis of achievement data shows what many had predicted — students lost academic ground after the spring of mostly virtual learning.
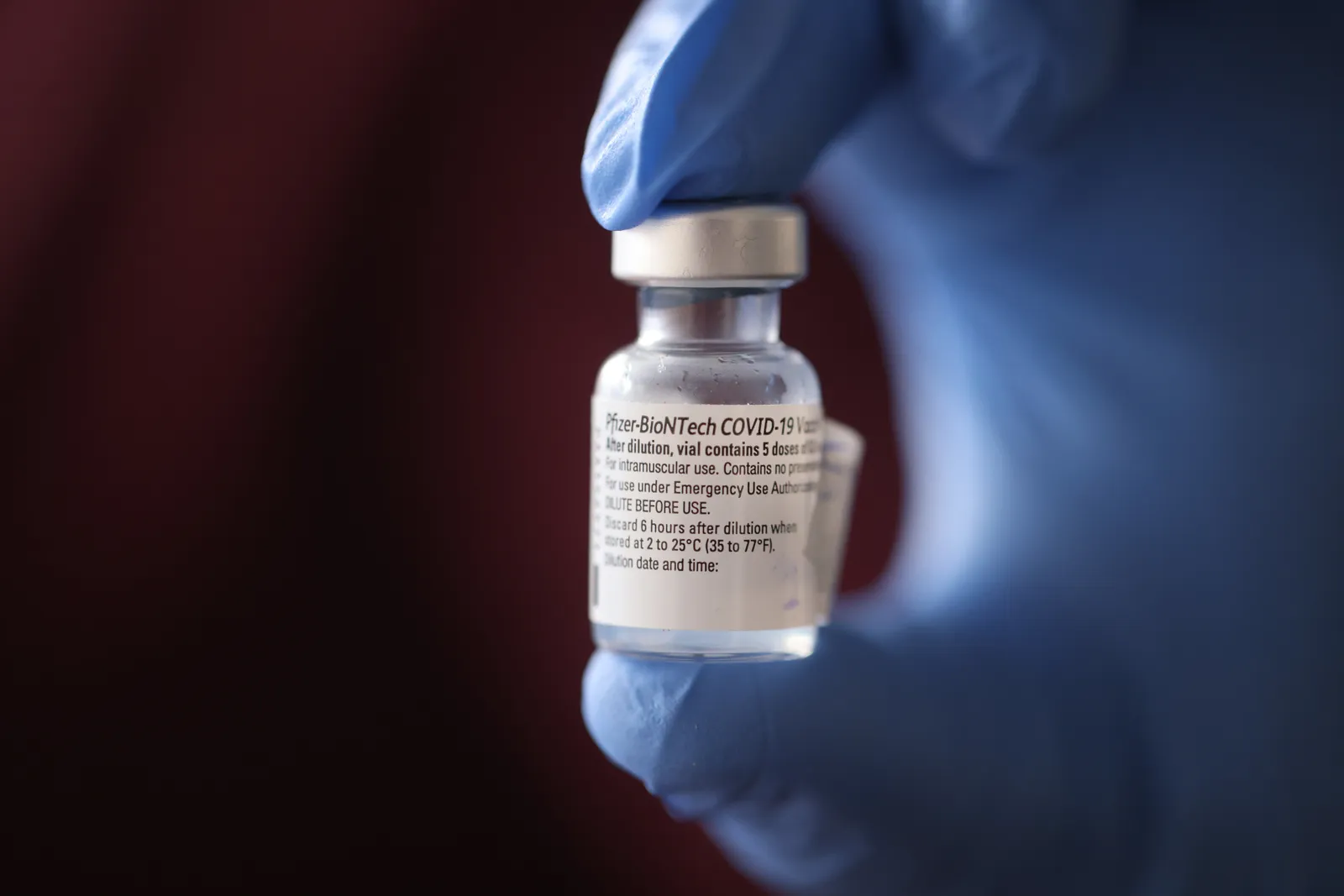
Dec. 11, 2020
Pfizer BioNTech receives emergency authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for COVID-19 vaccinations for people ages 16 and older. Schools begin discussing their roles in vaccination distribution and vaccine requirements for students and staff.
Dec. 27, 2020
The Coronavirus Response and Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act (CRRSA) is signed into law, giving schools $54.3 billion for continued efforts in providing in-person and virtual learning. These funds are also known as ESSER II.
January 2021
Data collected by the federal government shows 38% of 4th graders across the country were enrolled in full-time, in-person learning.

March 11, 2021
Exactly one year after the World Health Organization declared COVID a pandemic, the American Rescue Plan is signed into law. The legislation includes ESSER III, which at $121.9 billion is the largest one-time federal allocation ever given to U.S. schools. Together, the ESSER allocations add up to $189.5 billion.

May 2021
Slightly more than half (52%) of 4th graders across the country were enrolled in in-person, full-time learning.
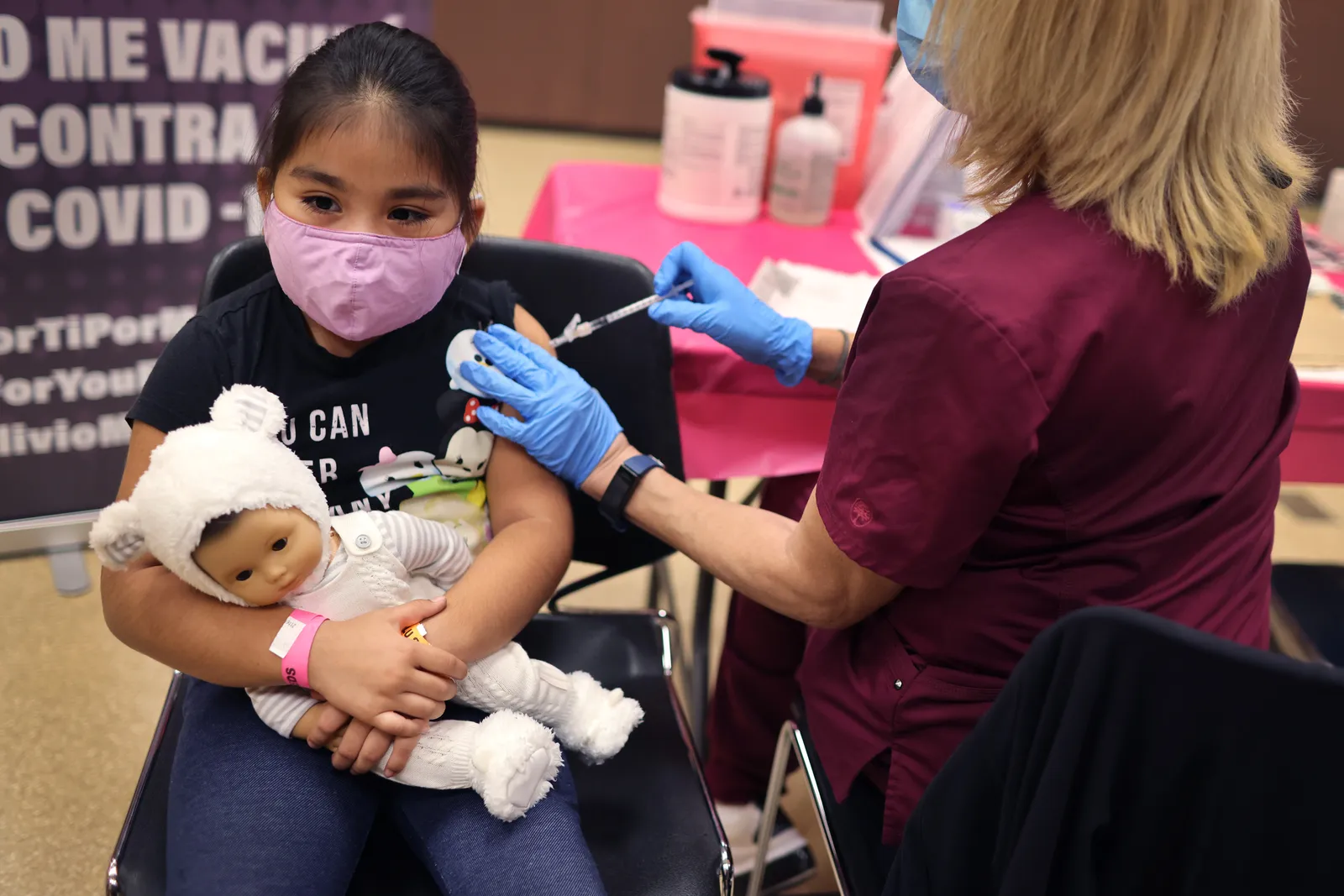
Oct. 29, 2021
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorizes the emergency use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine to include children ages 5 to 11 years.
December 2021
Close to 100% of 7,400 schools surveyed between September and December 2021 report their 4th- and 8th-grade students are enrolled in full-time, in-person instruction, according to data from the National Center for Education Statistics.

Feb. 25, 2022
The CDC announces updated COVID school guidance that only recommends mask requirements in communities with high levels of virus spread.
June 30, 2022
The federal nutrition waiver to provide universal school meals nationwide expires. Schools return to charging students for meals unless they qualify for free or reduced-price meals, and meal debt begins to build up again at the start of the 2022-23 academic year.
Fall 2022
Just as school administrators plan for a more typical year of in-person learning, a "tripledemic" of COVID, respiratory syncytial virus and flu causes widespread student and staff absences. Entire school systems shut down for in-person learning to minimize the illnesses' spread.
October 2022
Reading and math data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress for 4th and 8th grades confirm the extent of pandemic learning loss, with results described as "appalling and unacceptable" by U.S. Education Secretary Miguel Cardona at the time.
Feb. 10, 2023
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices officially recommends that COVID-19 vaccines be included in routine vaccinations for children ages 18 and younger.
April 13, 2023
CDC issues the most recent guidance for COVID-19 prevention in schools and childcare centers. The advice includes that schools promote equitable access to vaccinations, encourage those who are sick to stay home, improve indoor air quality, and promote hygiene and respiratory etiquette.
May 5, 2023
Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the World Health Organization’s director-general, announces in a media briefing that he is declaring the COVID-19 global health emergency over.
However, he notes the virus’s risks remain.
“Last week, COVID-19 claimed a life every three minutes — and that’s just the deaths we know about,” he says. “This virus is here to stay. It is still killing, and it’s still changing. The risk remains of new variants emerging that cause new surges in cases and deaths.”
May 11, 2023
The national emergency declaration for COVID comes to an end following a final extension by President Joe Biden in January 2023.